Research Proposal Sample | Medical Course | Part 1
Research Proposal Sample | Medical Course
Date:
Prepared by:
Name:
CHAPTER
I
Introduction
1.1. Background of the study
The rate of unemployed people, who are without work,
but who are available for work at current wages rate are increasing day by day.
According to the economic survey (2013-14), the
employment growth rate is only 2.9 per cent in Nepal. According to the central
bureau of statistics (CBS) 2014, age factor will be one of the reasons for
economic inactivity. Other reasons for economically inactive population are
studies household activities, being physically and mentally handicapped, sick
people and pension recipients. These group will not contribute to the
production of goods and services.
The problem is a burning challenge in Nepal as the
number of unemployed people are rapidly increasing. There are many causes of
unemployment. Firstly many people in Nepal engaged in agriculture areleaving
their occupation. They go to town to look for good job but they cannot get any
job easily and became unemployed. Secondly, some educated people are extremely
traditional and think that they should not do simple and are left jobless.
Thirdly, most of the students in Nepal lack technical and practical education.
Fourthly, the job opportunity is very limited.
The United Nation defines ‘youth’ as persons between
the ages of 15 to 24. The definition of youth varies across the globe; in
Nepal. The population in the age group 16 to 40 years is considered youth as
defined by national youth policy.
Every year Nepalese youth between 300000 to 350000
inter the job market. Only ten percent of them are absorbed in the domestic
market. More than one lakh of these leave the country in search of jobs and
rest remain here.
An economically active population (EAP) is defined by
the 2011 census as people of ten years of age and over who are active in
agricultural activities, wages/salary earnings, non-agricultural business
activities and those seeking jobs. Following this definition 26 percent of all
people were youth in 2008, making up nearly half of the economically active
population. In 2011, 28 percent of the total population of Nepal is in the age
group defined as youth, 54 percent of whom are girls and women.
Stress in psychology is defined as psychological
response experienced on encountering a threat that we feel we do not have the
resource to deal with.
If people do not get job there will be more chance of
suffering of mental disorders like anxiety, depression, panic disorder and
irritability. The physical health problem like hyper tension, diabetes,
cardiovascular diseases are more prevail to unemployed people. On the other
hand they are likely to involve crimes such as robbery theft etc. we can see
that unemployed youth are involved in drugs, smoking, drinking alcohol and even
commit suicide.
Coping has been defined in psychological terms by
Susan Folkman as Richard Lazarus as “constantly changing cognitive and
behavioural efforts to manage specific external and/or internal demand that are
appraised as taxing” or “exceeding the resources of the person”. Coping
strategy has been traditionally conceptualised as “adaptive” vs “maladaptive”
or as “problem focused” vs “emotion oriented” or “active” vs “avoidant”.
In order to solve the problem of unemployment, the
opportunities and facilities of technical education should be decentralised.
Youth should be encouraged to get technical education. In rural area, the
government obliged to encourage the people to establish cottage industries. For
the development of the nation, unemployed problem should be solved as soon as
possible.
1.2.
Rationale of the Study
According to the study of
youth survey Nepal 2011, 40.7 percent of youth of Nepal were unemployed and the
rate is still increasing. The problem of unemployment affect youth both
physically and mentally. The level of psychological stress amount youth may
begin with irritation, unable to concentrate, involvement in violence and
illegal activities, substance abuse, depression and lastly leads to suicide.
National survey of drug used
and health (2013) had concluded that 17 percent of unemployed workers had
substance abuse whereas only 9 percent of fulltime workers are involved in
substance abuse. On the other hand Nepal is in 8th ranked to have
highest suicidal rate in the world according to Psychbigyan network Nepal
(2015) in which one of the cause of suicide is unemployment. In a wider cross
sectional study done in India, it was concluded that women who were employed
but whose husband were unemployed were twice as likely to report physical
domestic violence compared to the women who were unemployed but whose husband
were employed. This study signifies that the level of stress and its reaction
varies between male and female as well as depends on the socio cultural
background.
In Nepal there are many
studies done on the topic of unemployment rate and causes of unemployment. But
there are no research studies done on the topic stress of unemployed youths and
how they are coping with this problems. So this study has to assess stress level
of unemployed youth and also provides information about how they are coping in
and effective or ineffective ways to decrease their stress level.
1.3. Statement of the Problem
While looking at the global scenario,unemployment statistics
show that percent of the total working population of USA, UK Japan are
unemployed.The unemployment rate of the USA is 4.9 per percent,UK 5.9percent, Germany4.7
percent. According to International labour organization (ILO). About 201
million people were unemployed in 2015 and will be more than 212 million people
by 2019.
The
government of Nepal defines youth as people between the ages of 16 to 40 years
but mostly considers age of 15 to 29 years. According to the youth survey 2011
done by the Nepal British Council, about 40.7 percent of the youth population
were completely unemployed and 4 lakhs young people entered the labor market
every year. Among the age range, 15 to 19 years, 57.1 percent were unemployed;
among 20 to 24 aged youth, 36.4 percent were not employed and among 25 to 29
years, 27.4 percent were not involved in income generating.
Among
those not involved in income generating activities 23.4 percent who comprised
this group cited lacked opportunities as main reason for unemployment, 12
percent due to lack of skill and training, 11.5 percent because of economic
condition while one percent due to lack of information. The problem of
unemployment leads to increase in stress level which includes irritation,
nervousness, depression that later result into involvement of substance abuse
and illegal activities and even suicides.
1.4. Objectives of the study
General
objectives
·
To assess stress and coping strategies
among unemployed youth.
Specific Objectives
·
To assess the level of stress among
unemployed youths.
·
To assess the type of coping strategies
among unemployed youths.
·
To determine the association of stress
level with selective socio demographic variables.
·
To determine the association of coping
strategies with selective socio demographic variables.
1.5. Research Questions
·
What is the level of stress among the
youths?
·
What are the coping strategies used by
unemployed youths?
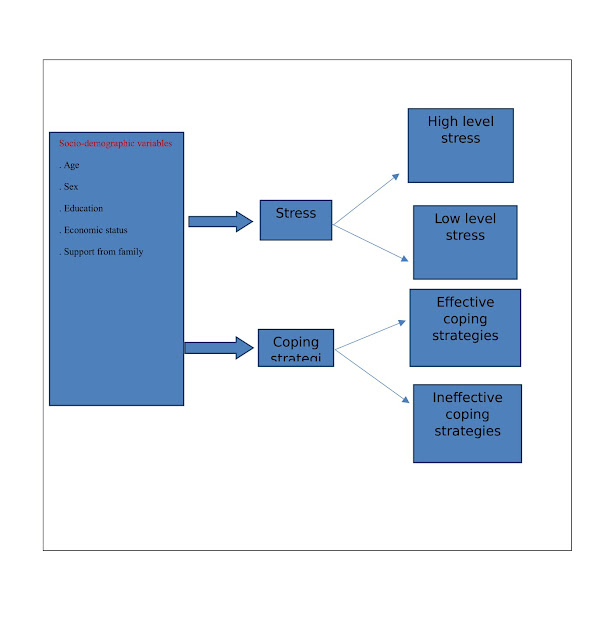
1.6. Study Variables
Dependent Variables: stress and coping strategies.
Independent Variables: age, sex, education, economic status, support from
family.
1.7.
Conceptual framework
Conceptual framework is the mental picture of the
phenomenon, formulated to illustrate the key concept of the study, here, the
independent variables are socio-demographic variables which include age, sex,
education, economic status and support from family which affect two dependent
variables, stress and coping strategies of unemployed youths. Then it is
determined that whether the level of stress is high level or low level. On the
other hand, it determined that whether the coping strategies are effective or
ineffective.
1.8. Operational definition
Youths: people
who have completed at least bachelor’s degree and are unemployed with 20 to 39
years of age.
Unemployed:youth
with no job as a source of income according to their qualification.
Stress:
any matter that cause tension, irritation or bad mood due to unemployment.
High level stress:
that scores more than an equal to 20 in perceived stress scale.
Low level stress:
stress that scores less than 20 in perceived stress scale.
Coping strategies:
different ways to deal with various stressors related to
Unemployment
which are either effective or ineffective coping strategies.
Effective coping strategies:
active coping strategies of brief cope scale used by unemployed youth that
include acceptance, emotional support, religion, active coping, planning,
positive reframing and instrumental support.
Ineffective coping strategies:
avoidant coping strategy of brief cope scale used by unemployed youth that
includes self-distraction, venting, humor, denial, behavioral dysfunction,
substance abuse and self-blame.
Low socio economic status:
family participants with income less than rupees10, 000
Middle economic status:participants
with family income between rupees 10,000 to 30,000
High economic status:participants
with family income more than rupees 30,000




Post a Comment